Ears Correction

A type of cosmetic surgery called ear correction surgery tries to change the shape or size of the ears, as well as realign them if they protrude. This surgical procedure is generally regarded as safe, and most people who have it say they are happy with the results. However, it is important to be aware of any hazards connected to the operation, and it is important to remember that there may be significant costs.
What is otoplasty?
Cosmetic ear surgery, commonly referred to as otoplasty, is a specialized procedure that focuses on enhancing the appearance of the external part of the ear known as the auricle. This intricate surgery aims to achieve desirable aesthetic changes and improve the overall balance and symmetry of the ears. By targeting the visible portion of the outer ear, otoplasty allows for tailored adjustments to create a harmonious and pleasing ear contour.
Otoplasty includes numerous different kinds of surgeries, each of which addresses a different issue:
- Ear augmentation: Occasionally, individuals may possess underdeveloped or smaller ears. Otoplasty offers a solution by increasing the size of the outer ear, allowing for a more proportionate appearance.
- Ear pinning: This form of otoplasty concentrates on repositioning the ears closer to the head. It is commonly sought by individuals whose ears noticeably protrude from the sides of their head, aiming to achieve a more balanced and natural ear contour.
- Ear reduction: Macrotia refers to a condition where the ears are larger than average. Those affected by macrotia may opt for otoplasty to reduce the size of their ears, bringing them into better harmony with the rest of their facial features.
How is Ear Surgery done?
Step 1: Anesthesia:

You will receive appropriate anesthesia, chosen based on your needs and preferences.
Step 2: Incision:

Surgical techniques are used to address protruding ears by creating or enhancing the antithetical fold and reducing enlarged conchal cartilage. Incisions are typically made on the back surface of the ear, with any front incisions placed within natural folds for minimal visibility. Internal sutures secure the newly shaped cartilage.
Step 3: Closing Incisions:
External stitches are used to close the incisions, with techniques tailored to preserve natural ear structures and achieve a balanced appearance.
Step 4: Results:
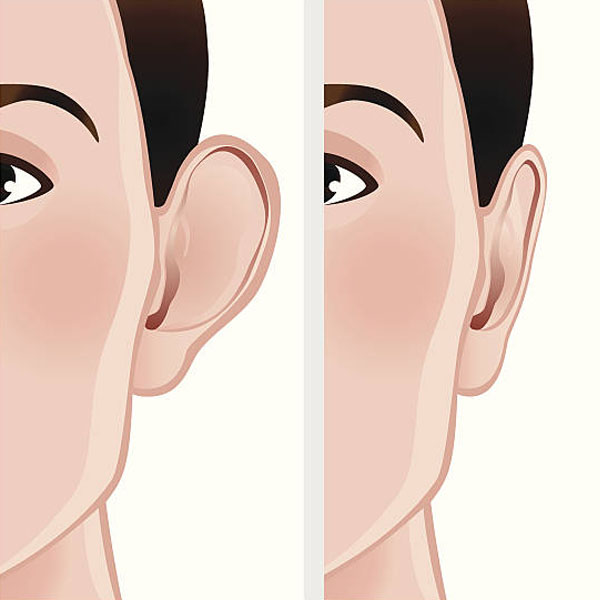
Immediate improvements can be seen once the dressings are removed. Repositioning the ear closer to the head minimizes visible scarring, hidden behind the ear or within natural creases.
What are the potential risks of Ear Correction Surgery?
- Infection: There is a risk of developing an infection at the surgical site, which may require antibiotics or further medical intervention.
- Bleeding: Excessive bleeding during or after the surgery is a potential risk. In rare cases, it may necessitate additional procedures to control the bleeding.
- Scarring: While efforts are made to minimize visible scarring, there is a possibility of noticeable scars at the incision sites. However, these scars typically fade over time and can often be concealed within natural creases.
- Changes in Sensation: Temporary or permanent changes in sensation around the ears, including numbness or hypersensitivity, may occur following otoplasty.
- Asymmetry or Dissatisfaction with Results: Despite the surgeon's best efforts, there is a chance of minor asymmetry or dissatisfaction with the aesthetic outcome of the surgery.
- Poor Wound Healing: Some individuals may experience delayed wound healing, which can lead to complications such as infection or increased scarring.
- Allergic Reactions: In rare cases, individuals may experience an allergic reaction to anesthesia, medications, or materials used during the surgery.
How much does ear surgery cost?
The ear surgery cost in India is influenced by several factors, including the specific procedure, the expertise and experience of the surgeon, the chosen hospital, and the type of anesthesia administered. Typically, the price range for ear surgery in India falls between Rs. 40,000 and Rs. 60,000. However, it's important to note that these figures are indicative and can vary depending on individual circumstances.
Frequently Asked Questions:
The recovery period following ear correction surgery varies from person to person. Generally, it takes about one to two weeks for initial healing, during which you may experience mild discomfort, swelling, or bruising. Most individuals can resume normal activities within a few days, but it's important to avoid strenuous activities or contact sports for several weeks to allow proper healing.
While incisions are made during ear correction surgery, skilled surgeons take great care to minimize visible scarring. Incisions are typically placed strategically behind the ear or within natural creases to make them less noticeable. Over time, any scars that do form tend to fade and become less visible.
Yes, otoplasty can address asymmetrical ears. Skilled surgeons can make precise adjustments to reshape and reposition the ears to achieve a more symmetrical appearance. During your consultation, your surgeon will assess your specific situation and discuss the expected outcomes based on your individual needs.
In most cases, the results of ear correction surgery are permanent. Once the ears are repositioned or reshaped, they typically maintain their new appearance long-term. However, it's important to note that natural aging processes can still affect the ears over time.
Ear correction surgery is suitable for both children and adults. While the procedure is commonly performed on children before the age of 14, adults can also benefit from otoplasty. The candidacy for surgery is determined on an individual basis, and a consultation with a qualified surgeon will help determine the best approach for each patient, regardless of age.
Procedure Time:
- 2-5 hours
Full Recovery:
- 6 weeks
Anaesthetic:
• General
Back to work:
• After 2 weeks
Duration of results:
• Permanent
Results:
• Noticeable within 2 weeks
Temporary risks & complications:
• May include soreness, bleeding, persistent pain, and infection
• *Individual results and reactions may vary.