Breast Reconstruction
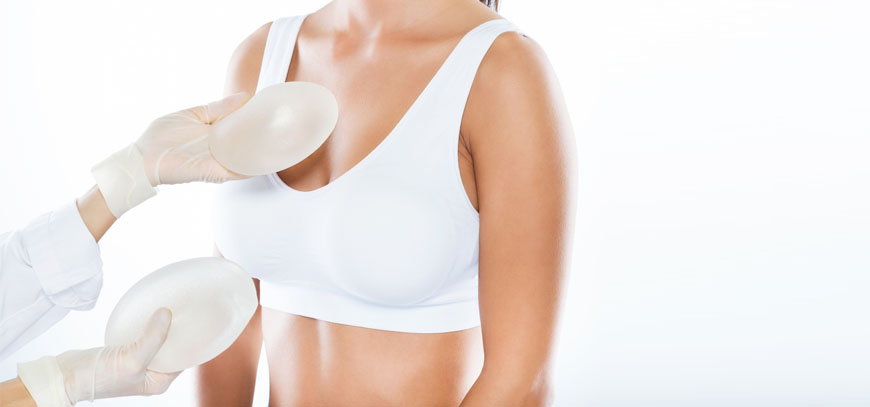

Breast reconstruction is a surgical procedure aimed at restoring the appearance of breasts following a mastectomy. There exist various types of breast reconstruction techniques available to patients. Some methods involve the use of implants, while others utilize tissue sourced from the individual's own body, such as the abdominal area, to create a reconstructed breast. The timing of breast reconstruction can vary, with some individuals opting for immediate reconstruction after a mastectomy, while others may choose to undergo the procedure later. It's important to note that breast reconstruction often involves multiple surgeries that may be spread out over several months, ensuring a comprehensive and successful outcome.
What is breast reconstruction?
Breast reconstruction is a surgical intervention designed to restore the shape and appearance of the breasts after a mastectomy or lumpectomy procedure. In certain cases, multiple surgeries may be required to achieve the desired outcome. Various techniques are available for breast reconstruction, offering individuals a range of options. One approach involves the use of silicone or saline breast implants, which can effectively recreate breast volume. Alternatively, some techniques involve the transfer of tissue from another part of the body, such as the lower abdominal region, in the form of a flap to reconstruct the breast.
Different types of breast reconstruction surgery
Breast reconstruction surgeries after mastectomies can be classified into two main types:
- Flap reconstruction
- Implant reconstruction
Flap reconstruction involves using autologous tissue, taken from various parts of the body such as the lower abdomen, thigh, back, or buttocks, to form a new breast. The tissue, known as a flap, may include fat, skin, blood vessels, and muscle. Flaps can be moved with their own blood supply (pedicled flap) or detached and reattached to blood vessels in the chest (free flap). Different types of flap reconstruction include DIEP, TRAM, Latissimus dorsi (LD), IGAP, SGAP, PAP, TUG, and SIEA/SIEP flaps.
Implant reconstruction, on the other hand, involves using saline or silicone implants to recreate breast tissue. This method may also combine implants with tissue from the patient's body. Implant reconstruction can be performed concurrently with a mastectomy or later. It can be done either beneath the chest muscle or on top of it. Another approach is using a tissue expander initially, which gradually stretches the skin until it is ready to receive the implant.
How is Breast Reconstruction Procedure done?
How is Breast Reconstruction Procedure done?

Step 1 - Anesthesia
During the surgical procedure, appropriate anesthesia will be administered to ensure your comfort. Your doctor will determine the most suitable option, which may include intravenous sedation or general anesthesia.
Step 2 - Flap techniques for breast mound creation
In cases where there is insufficient tissue on the chest wall after mastectomy or radiation therapy, breast reconstruction typically involves flap techniques or tissue expansion. Flap techniques involve repositioning the patient's own tissue to create or cover the breast mound. Options include:
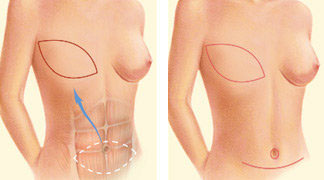
TRAM flap: This technique uses muscle, fat, and skin from the donor site usually a women’s lower abdomen to reconstruct the breast. The flap can either remain connected to the original blood supply and be tunneled through the bottom of the chest wall or be detached and formed into a breast mound. Alternatively, the DIEP flap or SIEA flap techniques may be employed, which involve transferring only skin and fat from the abdomen without using abdominal muscle. If there is insufficient tissue in the lower abdomen, other donor sites like the buttocks or thighs can be considered (SGAP flap, TUG flap, PAP flap).

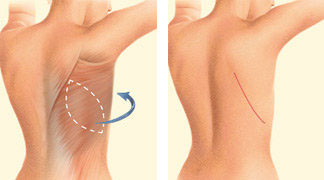
Latissimus dorsi flap: This technique uses muscle, fat, and skin from the back underneath the shoulder, which is tunneled to the mastectomy site while keeping the blood supply intact. The latissimus flap provides the necessary tissue to cover and support a breast implant, although it may not always create a complete breast mound.v
Step 3 – Tissue expansion for skin stretching
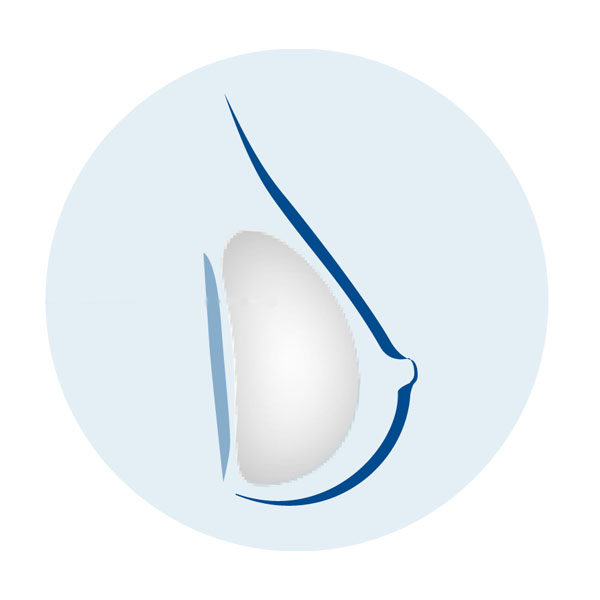
Tissue expansion is an option for women who don't require breast radiation and wish to avoid using a separate donor site. This approach involves gradually stretching healthy skin to provide coverage for a breast implant. It typically requires multiple office visits over 1-2 months to fill the expander with saline. In some cases, air-filled devices allow patients to self-expand the skin at home with a remote dosage controller. A second surgery will be needed to replace the expander if it's not designed as a permanent implant.
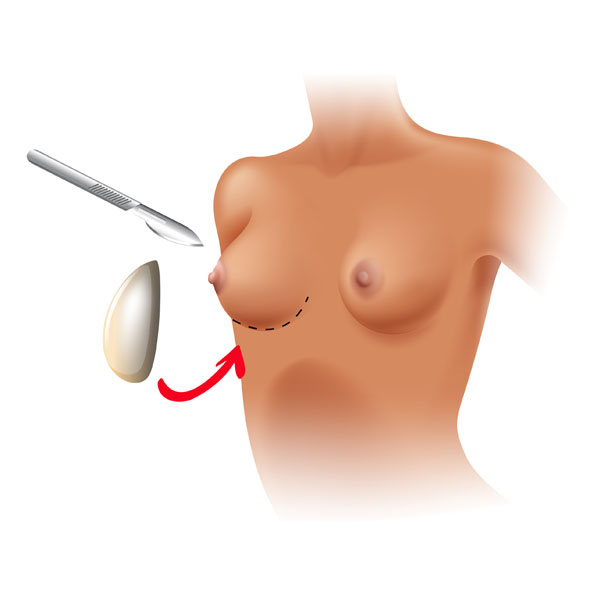
Step 4 – Placement of a breast implant
Breast implants can be used in addition to or as an alternative to flap techniques. Surgeons may also use implants as temporary placeholders during other breast cancer treatments before more complex flap reconstruction techniques. Saline and silicone implants are available for reconstruction, and your surgeon will help determine the most suitable option for you. Reconstruction with an implant alone often requires tissue expansion. Direct-to-implant breast reconstruction may be an ideal reconstructive option for certain tumor characteristics and breast shapes.
Step 5 – Nipple and areola reconstruction, breast revision techniques
For individuals who aren't suitable candidates for nipple-sparing mastectomy, breast reconstruction is completed using various techniques to reconstruct the nipple and areola. These techniques typically involve folding skin to create a nipple shape and are followed by tattooing. Three-dimensional nipple-areolar tattooing alone can be used to create the appearance of a realistic nipple with the illusion of projection. Staged revision procedures may be employed to enhance symmetry, utilize liposuction with fat grafting, and improve the appearance of the donor site, further enhancing breast reconstruction outcomes.
What are the benefits of Breast Reconstruction Surgery?
- Breast reconstruction surgery after mastectomy or lumpectomy can boost self-confidence.
- It improves how clothes fit and increases comfort in wearing swimsuits.
- Some individuals prefer wearing a breast form (prosthesis) with a special bra instead of undergoing reconstruction.
- Others choose to embrace a "flat" appearance and opt not to wear prosthetic breasts.
- The decision regarding breast reconstruction or alternative options is highly personal and varies from person to person.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Breast reconstruction surgery in India generally costs over Rs 80,000. Private hospital fees can range from Rs. 100,000 to 500,000 depending on the procedure and facility. The cost may double when reconstructing both breasts in one sitting for hereditary breast cancer patients. Actual prices may vary based on location, surgeon, and hospital factors.
Yes, breast reconstruction surgery is often covered by insurance plans in India. It is important to check with your specific insurance provider to understand the coverage details and any potential requirements or limitations.
The recovery period after breast reconstruction surgery varies depending on the individual and the type of procedure performed. Generally, it can take several weeks to a few months for the initial healing process. Full recovery and the return to normal activities may take several months.
Like any surgical procedure, breast reconstruction surgery carries some risks and potential complications. These can include infection, bleeding, scarring, implant-related issues, changes in breast sensation, and asymmetry. It is important to discuss these associated risks with your surgeon before undergoing the procedure.
In many cases, breast reconstruction surgery can be performed even if a person has had a previous breast augmentation or reduction surgery. The feasibility and specific approach would depend on individual factors and the surgeon's assessment.
The timing of breast reconstruction surgery can vary. It can be performed immediately following a mastectomy (immediate reconstruction) or delayed until a later time (delayed reconstruction). The decision depends on several factors, including the individual's overall health, cancer treatment plan, and personal preferences. It is important to discuss the options with your healthcare team to determine the most suitable timing for your situation
Procedure Time:
- 2-5 hours
Full Recovery:
- 6 weeks
Anaesthetic:
• General
Back to work:
• After 2 weeks
Duration of results:
• Permanent
Results:
• Noticeable within 2 weeks
Temporary risks & complications:
• May include soreness, bleeding, persistent pain, and infection
• *Individual results and reactions may vary.